A data structure is a storage that is used to store and organize data. It is a way of arranging data on a computer so that it can be accessed and updated efficiently.
A data structure is not only used for organizing the data. It is also used for processing, retrieving, and storing data. There are different basic and advanced types of data structures that are used in almost every program or software system that has been developed.
Data structures are an integral part of computers used for the arrangement of data in memory. They are essential and responsible for organizing, processing, accessing, and storing data efficiently. But this is not all. Various types of data structures have their own characteristics, features, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. So how do you identify a data structure that is suitable for a particular task? What is meant by the term ‘Data Structure’? How many types of data structures are there and what are they used for?
How Data Structure varies from Data Type
| Data Type | Data Structure |
|---|---|
| The data type is the form of a variable to which a value can be assigned. It defines that the particular variable will assign the values of the given data type only. | Data structure is a collection of different kinds of data. That entire data can be represented using an object and can be used throughout the program. |
| It can hold value but not data. Therefore, it is dataless. | It can hold multiple types of data within a single object. |
| The implementation of a data type is known as abstract implementation. | Data structure implementation is known as concrete implementation. |
| There is no time complexity in the case of data types. | In data structure objects, time complexity plays an important role. |
| In the case of data types, the value of data is not stored because it only represents the type of data that can be stored. | While in the case of data structures, the data and its value acquire the space in the computer’s main memory. Also, a data structure can hold different kinds and types of data within one single object. |
| Data type examples are int, float, double, etc. | Data structure examples are stack, queue, tree, etc. |
Classification of Data Structure

- Linear data structure – Data structure in which data elements are arranged sequentially or linearly, where each element is attached to its previous and next adjacent elements, is called a linear data structure.
- Static data structure: Static data structure has a fixed memory size. It is easier to access the elements in a static data structure.
- Dynamic data structure: In dynamic data structure, the size is not fixed. It can be randomly updated during the runtime which may be considered efficient concerning the memory (space) complexity of the code.
- Non-linear data structure – Data structures where data elements are not placed sequentially or linearly are called non-linear data structures. In a non-linear data structure, we can’t traverse all the elements in a single run only.
Need Of Data structure
The structure of the data and the synthesis of the algorithm are relative to each other. Data presentation must be easy to understand so the developer, as well as the user, can make an efficient implementation of the operation. Data structures provide an easy way of organizing, retrieving, managing, and storing data.
- Data structure modification is easy.
- It requires less time.
- Save storage memory space.
- Data representation is easy.
- Easy access to the large database.
Advantages of Data structure
- Improved data organization and storage efficiency.
- Faster data retrieval and manipulation.
- Facilitates the design of algorithms for solving complex problems.
- Eases the task of updating and maintaining the data.
- Provides a better understanding of the relationships between data elements.
Disadvantage of Data Structure
- Increased computational and memory overhead.
- Difficulty in designing and implementing complex data structures.
- Limited scalability and flexibility.
- Complexity in debugging and testing.
- Difficulty in modifying existing data structures.
Arrays:
An array is a linear data structure and it is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together in one place. It allows the processing of a large amount of data in a relatively short period. The first element of the array is indexed by a subscript of 0. There are different operations possible in an array, like Searching, Sorting, Inserting, Traversing, Reversing, and Deleting.

Characteristics of an Array:
An array has various characteristics which are as follows:
- Arrays use an index-based data structure which helps to identify each of the elements in an array easily using the index.
- If a user wants to store multiple values of the same data type, then the array can be utilized efficiently.
- An array can also handle complex data structures by storing data in a two-dimensional array.
- An array is also used to implement other data structures like Stacks, Queues, Heaps, Hash tables, etc.
- The search process in an array can be done very easily.
Operations performed on array
- Initialization: An array can be initialized with values at the time of declaration or later using an assignment statement.
- Accessing elements: Elements in an array can be accessed by their index, which starts from 0 and goes up to the size of the array minus one.
- Searching for elements: Arrays can be searched for a specific element using linear search or binary search algorithms.
- Sorting elements: Elements in an array can be sorted in ascending or descending order using algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, or quick sort.
- Inserting elements: Elements can be inserted into an array at a specific location, but this operation can be time-consuming because it requires shifting existing elements in the array.
- Deleting elements: Elements can be deleted from an array by shifting the elements that come after it to fill the gap.
- Updating elements: Elements in an array can be updated or modified by assigning a new value to a specific index.
- Traversing elements: The elements in an array can be traversed in order, visiting each element once.
Linked list:
A linked list is a linear data structure in which elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers as shown in the below image:
Types of linked lists:
- Singly-linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Circular linked list
- Doubly circular linked list
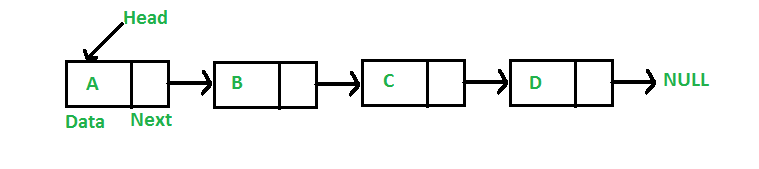
Linked List
Characteristics of a Linked list:
A linked list has various characteristics which are as follows:
- A linked list uses extra memory to store links.
- During the initialization of the linked list, there is no need to know the size of the elements.
- Linked lists are used to implement stacks, queues, graphs, etc.
- The first node of the linked list is called the Head.
- The next pointer of the last node always points to NULL.
- In a linked list, insertion and deletion are possible easily.
- Each node of the linked list consists of a pointer/link which is the address of the next node.
- Linked lists can shrink or grow at any point in time easily.
Operations performed on Linked list:
A linked list is a linear data structure where each node contains a value and a reference to the next node. Here are some common operations performed on linked lists:
- Initialization: A linked list can be initialized by creating a head node with a reference to the first node. Each subsequent node contains a value and a reference to the next node.
- Inserting elements: Elements can be inserted at the head, tail, or at a specific position in the linked list.
- Deleting elements: Elements can be deleted from the linked list by updating the reference of the previous node to point to the next node, effectively removing the current node from the list.
- Searching for elements: Linked lists can be searched for a specific element by starting from the head node and following the references to the next nodes until the desired element is found.
- Updating elements: Elements in a linked list can be updated by modifying the value of a specific node.
- Traversing elements: The elements in a linked list can be traversed by starting from the head node and following the references to the next nodes until the end of the list is reached.
- Reversing a linked list: The linked list can be reversed by updating the references of each node so that they point to the previous node instead of the next node.
Real-Life Applications of a Linked list:
- A linked list is used in Round-Robin scheduling to keep track of the turn in multiplayer games.
- It is used in image viewer. The previous and next images are linked, and hence can be accessed by the previous and next buttons.
- In a music playlist, songs are linked to the previous and next songs.
Stack Data Structure
Stack is a linear data structure that follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is LIFO(Last in first out). Entering and retrieving data is possible from only one end. The entering and retrieving of data is also called push and pop operation in a stack. There are different operations possible in a stack like reversing a stack using recursion, Sorting, Deleting the middle element of a stack, etc.

Characteristics of a Stack
Stack has various different characteristics which are as follows:
- Stack is used in many different algorithms like Tower of Hanoi, tree traversal, recursion, etc.
- Stack is implemented through an array or linked list.
- It follows the Last In First Out operation i.e., an element that is inserted first will pop in last and vice versa.
- The insertion and deletion are performed at one end i.e. from the top of the stack.
- In stack, if the allocated space for the stack is full, and still anyone attempts to add more elements, it will lead to stack overflow.
Operation performed on stack
A stack is a linear data structure that implements the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle. Here are some common operations performed on stacks:
- Push: Elements can be pushed onto the top of the stack, adding a new element to the top of the stack.
- Pop: The top element can be removed from the stack by performing a pop operation, effectively removing the last element that was pushed onto the stack.
- Peek: The top element can be inspected without removing it from the stack using a peek operation.
- IsEmpty: A check can be made to determine if the stack is empty.
- Size: The number of elements in the stack can be determined using a size operation.
Real-Life Applications of Stack
- Real life example of a stack is the layer of eating plates arranged one above the other. When you remove a plate from the pile, you can take the plate to the top of the pile. But this is exactly the plate that was added most recently to the pile. If you want the plate at the bottom of the pile, you must remove all the plates on top of it to reach it.
- Browsers use stack data structures to keep track of previously visited sites.
- Call log in mobile also uses stack data structure.
Queue Data Structure
Queue is a linear data structure that follows a particular order in which the operations are performed. The order is First In First Out(FIFO) i.e. the data item stored first will be accessed first. In this, entering and retrieving data is not done from only one end. An example of a queue is any queue of consumers for a resource where the consumer that came first is served first. Different operations are performed on a Queue like Reversing a Queue (with or without using recursion), Reversing the first K elements of a Queue, etc. A few basic operations performed In Queue are enqueue, dequeue, front, rear, etc.

Characteristics of a Queue
The queue has various different characteristics which are as follows:
- The queue is a FIFO (First In First Out) structure.
- To remove the last element of the Queue, all the elements inserted before the new element in the queue must be removed.
- A queue is an ordered list of elements of similar data types.
Operation performed on queue
A queue is a linear data structure that implements the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle. Here are some common operations performed on queues:
- Enqueue: Elements can be added to the back of the queue, adding a new element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue: The front element can be removed from the queue by performing a dequeue operation, effectively removing the first element that was added to the queue.
- Peek: The front element can be inspected without removing it from the queue using a peek operation.
- IsEmpty: A check can be made to determine if the queue is empty.
- Size: The number of elements in the queue can be determined using a size operation.
Real-Life Applications of Queue
- A real-world example of a queue is a single-lane one-way road, where the vehicle that enters first will exit first.
- A more real-world example can be seen in the queue at the ticket windows.
- A cashier line in a store is also an example of a queue.
- People on an escalator
Tree Data Structure
A tree is a non-linear and hierarchical data structure where the elements are arranged in a tree-like structure. In a tree, the topmost node is called the root node. Each node contains some data, and data can be of any type. It consists of a central node, structural nodes, and sub-nodes which are connected via edges. Different tree data structures allow quicker and easier access to the data as it is a non-linear data structure. A tree has various terminologies like Node, Root, Edge, Height of a tree, Degree of a tree, etc.
There are different types of Tree-like
- Binary Tree,
- Binary Search Tree,
- AVL Tree,
- B-Tree, etc.

Characteristics of a Tree Data Structure
The tree has various different characteristics which are as follows:
- A tree is also known as a Recursive data structure.
- In a tree, the Height of the root can be defined as the longest path from the root node to the leaf node.
- In a tree, one can also calculate the depth from the top to any node. The root node has a depth of 0.
Operation performed on Tree
A tree is a non-linear data structure that consists of nodes connected by edges. Here are some common operations performed on trees:
- Insertion: New nodes can be added to the tree to create a new branch or to increase the height of the tree.
- Deletion: Nodes can be removed from the tree by updating the references of the parent node to remove the reference to the current node.
- Search: Elements can be searched for in a tree by starting from the root node and traversing the tree based on the value of the current node until the desired node is found.
- Traversal: The elements in a tree can be traversed in several different ways, including in-order, pre-order, and post-order traversal.
- Height: The height of the tree can be determined by counting the number of edges from the root node to the furthest leaf node.
- Depth: The depth of a node can be determined by counting the number of edges from the root node to the current node.
- Balancing: The tree can be balanced to ensure that the height of the tree is minimized and the distribution of nodes is as even as possible.
Real-Life Applications of Tree
- In real life, tree data structure helps in Game Development.
- It also helps in indexing in databases.
- A Decision Tree is an efficient machine-learning tool, commonly used in decision analysis. It has a flowchart-like structure that helps to understand data.
- Domain Name Server also uses a tree data structure.
- The most common use case of a tree is any social networking site.
Graph Data Structure
A graph is a non-linear data structure that consists of vertices (or nodes) and edges. It consists of a finite set of vertices and set of edges that connect a pair of nodes. The graph is used to solve the most challenging and complex programming problems. It has different terminologies which are Path, Degree, Adjacent vertices, Connected components, etc.

Graph
Characteristics of Graph
The graph has various different characteristics which are as follows:
- The maximum distance from a vertex to all the other vertices is considered the Eccentricity of that vertex.
- The vertex having minimum Eccentricity is considered the central point of the graph.
- The minimum value of Eccentricity from all vertices is considered the radius of a connected graph.
Applications of Graph
Different applications of Graphs are as follows:
- The graph is used to represent the flow of computation.
- It is used in modeling graphs.
- The operating system uses Resource Allocation Graph.
- Also used in the World Wide Web where the web pages represent the nodes.
Operation performed on Graph
A graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of nodes and edges. Here are some common operations performed on graphs:
- Add Vertex: New vertices can be added to the graph to represent a new node.
- Add Edge: Edges can be added between vertices to represent a relationship between nodes.
- Remove Vertex: Vertices can be removed from the graph by updating the references of adjacent vertices to remove the reference to the current vertex.
- Remove Edge: Edges can be removed by updating the references of the adjacent vertices to remove the reference to the current edge.
- Depth-First Search (DFS): A graph can be traversed using a depth-first search by visiting the vertices in a depth-first manner.
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): A graph can be traversed using a breadth-first search by visiting the vertices in a breadth-first manner.
- Shortest Path: The shortest path between two vertices can be determined using algorithms such as Dijkstra’s algorithm or A* algorithm.
- Connected Components: The connected components of a graph can be determined by finding sets of vertices that are connected to each other but not to any other vertices in the graph.
- Cycle Detection: Cycles in a graph can be detected by checking for back edges during a depth-first search.
Real-Life Applications of Graph
- One of the most common real-world examples of a graph is Google Maps where cities are located as vertices and paths connecting those vertices are located as edges of the graph.
- A social network is also one real-world example of a graph where every person on the network is a node, and all of their friendships on the network are the edges of the graph.
- A graph is also used to study molecules in physics and chemistry.
Conclusion
Although these are the most widely known and used data structures, there are some other forms of data structures as well which are used in Computer Science, such as policy-based data structures, etc. But no matter which data structure you choose, each one has its perks and disadvantages, without the knowledge of which, it can be very costly to choose the wrong type of data structure. So it is very important to understand the need of the situation, and then decide which kind of data structure suits best for the job.
For more know contact Us.



Pingback: Queue Data Structure - SKB Development
Pingback: Stack Data Structure - SKB Development
Pingback: Singly Link List Data Structure - SKB Development
aut et iste nesciunt aut enim ea. velit odit et ipsa dignissimos atque ipsa ex incidunt unde suscipit omnis aut dolores sit omnis. ut ut inventore et nisi accusamus nihil iste et et.
eveniet laboriosam sint autem reiciendis quam nam suscipit accusantium porro inventore aut. enim velit ea et eum pariatur maiores rem provident qui dolorum saepe ut velit distinctio sint laborum rerum
est dolorem in magnam autem et ex accusantium aut laudantium error consectetur. cupiditate aspernatur et qui inventore est. in repudiandae voluptas asperiores ut aspernatur laborum. blanditiis atque i
recusandae asperiores modi optio voluptas incidunt ut commodi a cum beatae doloribus odit voluptatibus consequatur est occaecati aut explicabo. incidunt soluta rerum saepe veritatis minima dicta asper
et delectus error voluptas voluptatem quia et sit. magni aperiam commodi quam odio suscipit eligendi non fugit inventore quo dolor facilis cum ducimus id molestiae. ea quis id et et eligendi deleniti