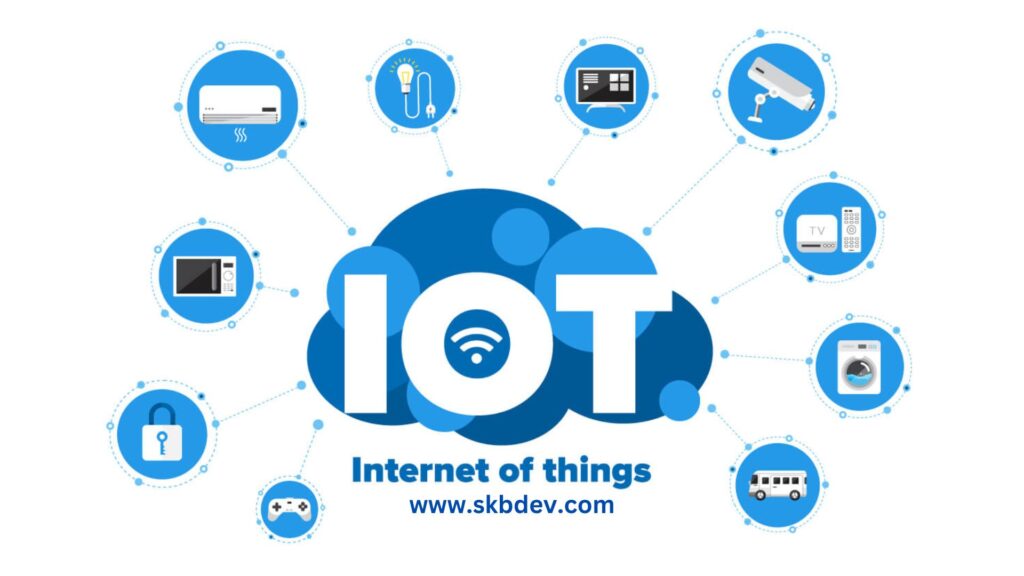
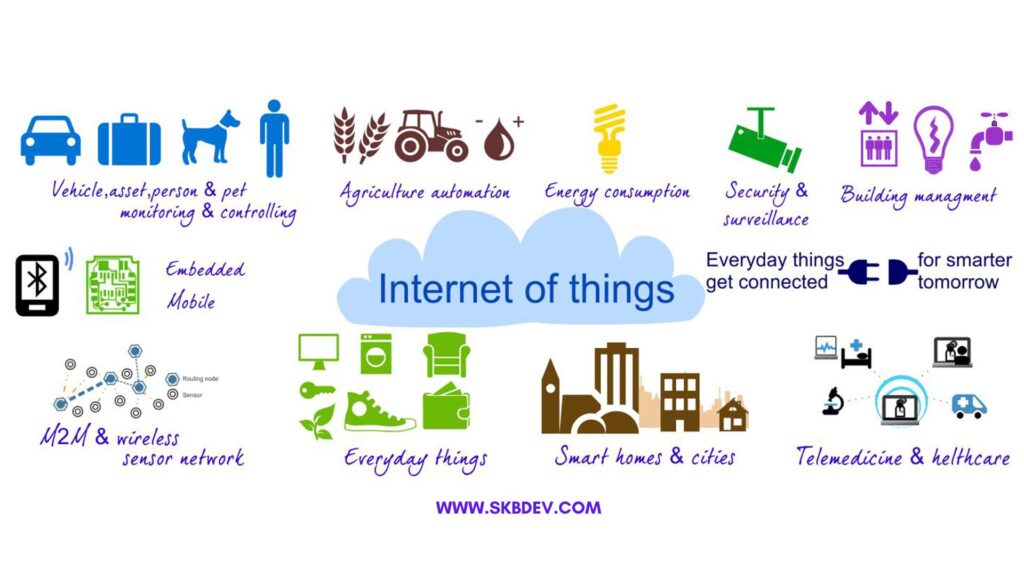
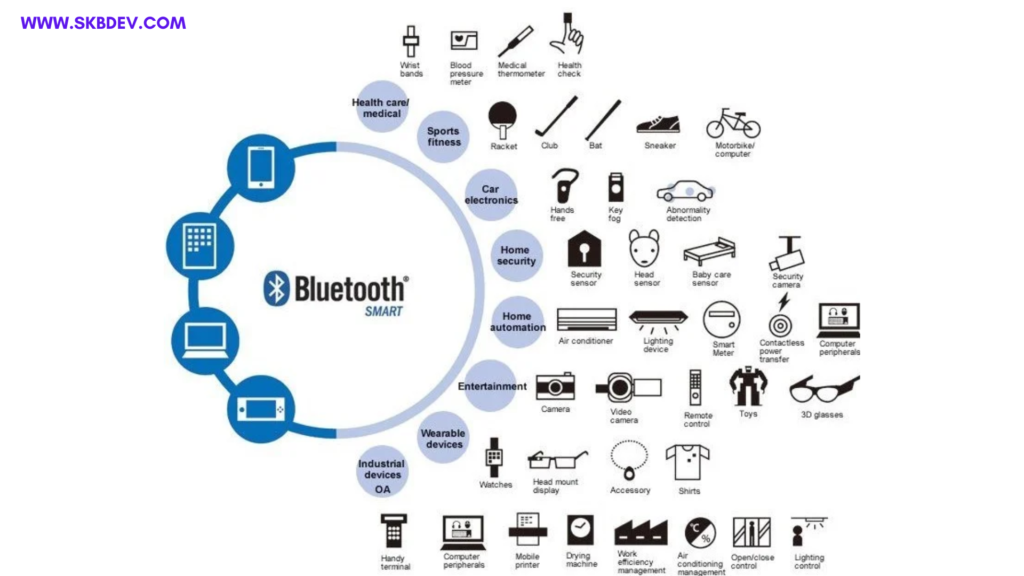
What would IoT be without IoT sensors? The answer is: nothing. Sensor are the foundation of an IoT ecosystem, providing devices with the ability to collect the data used to make things happen. Let’s take a look at IoT sensors in detail, including the types of sensors available, how they’re used, and examples of IoT sensors in the real world.
Sensor
A sensor is a device that detects and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The input can be light, heat, motion, moisture, pressure or any number of other environmental phenomena. The output is generally a signal that is converted to a human-readable display at the sensor location or transmitted electronically over a network for reading or further processing.

Types of Sensors
There are many different types of sensors, and they come in different shapes and sizes. Here are 13 of the most common types and uses of sensors.
Temperature Sensor
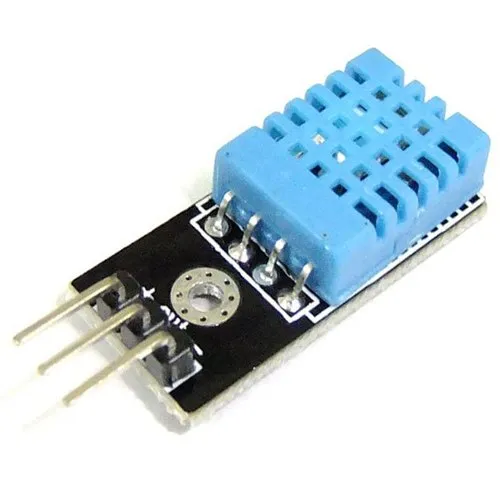
Temperature sensors measure the amount of heat generated from an area or an object. They detect a temperature change and convert the findings to data. Temperature sensors are used in various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture. Some examples are thermistors, thermocouples, and resistor temperature detectors (RTD).
Proximity Sensor
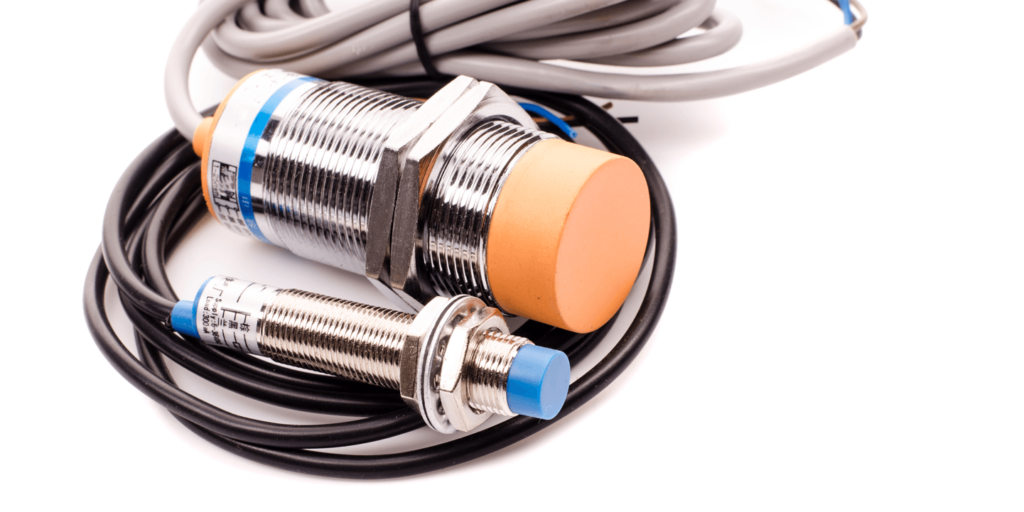

Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects near the sensor without physical contact. They often emit a beam of radiation like infrared or an electromagnetic field. They can be used for process monitoring and control, object counting, assembly lines, and determining available space. Proximity sensors are common in retail settings, industrial complexes, and parking lots. Some examples are photoelectric, magnetic, capacitive, inductive, and ultrasonic.
Pressure Sensors
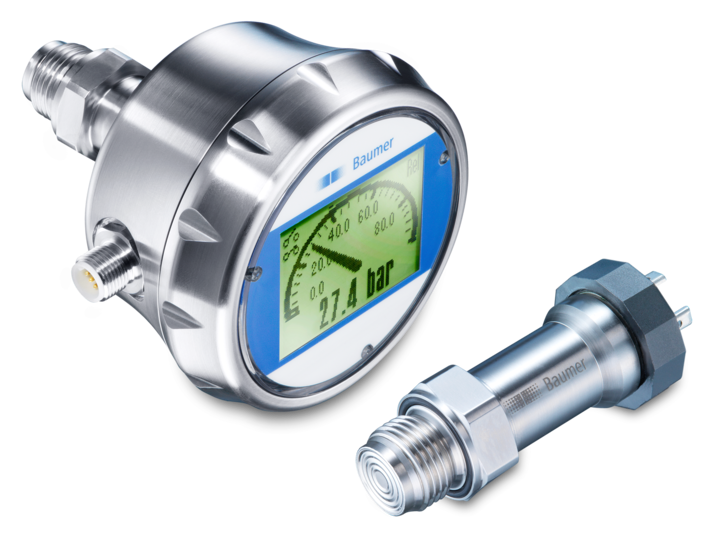

These sensors detect changes in a gas or liquid. When the pressure range is beyond a set threshold, pressure sensors alert to the problem. They are used for leak testing, water systems, vehicles, and aircraft. For example, the BMP180 is a digital pressure sensor found in cell phones and GPS navigation devices. And some vehicles use a tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) to alert when tire pressure is low and potentially unsafe.
Water Quality Sensors
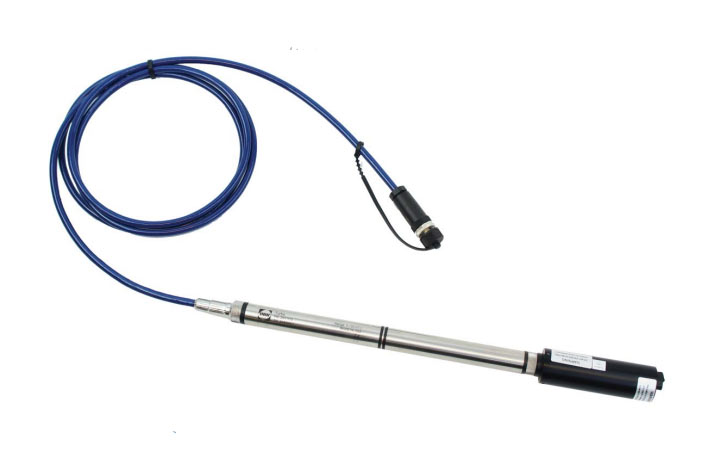

As you’d expect, water quality sensors monitor the quality of water. They are often used in water distribution systems, but they function in a variety of industries. There are different kinds of water sensors, including residual chlorine sensors, turbidity sensors, pH sensors, and total organic carbon sensors.
Chemical and Gas Sensor

These sensors monitor air quality for the presence of toxic or hazardous gas. They often use semiconductor, electrochemical, or photo-ionization technologies for detection. They are typically used in industrial and manufacturing settings, though they are also found in carbon dioxide detectors.
Infrared Sensors

Some sensors either detect or emit infrared radiation to sense characteristics and changes in the surrounding area. They’re useful for measuring heat emissions from an object. Infrared sensors are used in remote controls, healthcare settings, and even by art historians authenticating artwork.
Smoke Sensors

Most people are familiar with smoke detectors, as they have protected our homes and businesses for a long time. However, with improvements based on IoT, smoke detectors are now more user-friendly, convenient, and wire-free.
Motion Sensors

Motion sensors detect physical movement in an area. Of course, these sensors play a significant role in the security industry, but they are used in nearly every industry. Applications include automated sinks and toilet flushers, automatic door controls, energy management systems, and automated parking systems. Standard motion sensors include ultrasonic, microwave, and passive infrared (PIR).
Image Sensors
These sensors convert optical images into signals and are generally used to display or store files electronically. They are found in radar and sonar, biometric devices, night vision equipment, medical imaging, digital cameras, and even some cars. Charge-coupled devices (CCD) and complementary metal-oxide semiconductors (CMOS) are most commonly used.
Humidity Sensors
These sensors measure the amount of water vapor in the air. Typical uses include heating and air conditioning systems (HVAC) and weather monitoring and prediction. When humidity must be tightly controlled, such as in museums, hospitals, and greenhouses, humidity sensors assist the process.
Accelerometer Sensor
Accelerometer sensors detect the orientation of an object and the rate of change, including tap, shake, tilt, and positioning. They are used in many industries for smart pedometers, anti-theft protection, and monitoring auto fleets. Some types are capacitive accelerometers and hall-effect accelerometers.
Gyroscope Sensors

A gyroscope sensor measures the angular rate or velocity, or the speed of rotation around an axis. They are generally used for navigation in the auto industry for navigation and anti-skid systems as well as in video games and drones. Some examples include optical gyroscopes, rotary gyroscopes, and vibrating structure gyroscopes.
Optical Sensors

Optical sensors measure light and convert it into electrical signals. Many industries make use of optical sensors, including auto, energy, healthcare, and aerospace. Sensors include fiber optics, photodetector, and pyrometer.